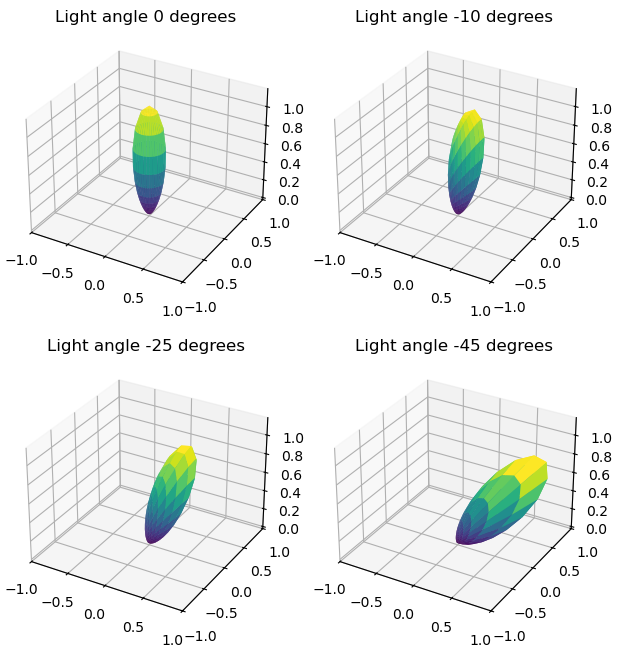
3D surface BRDF plots
This example demonstrates how to make 3D surface plots of sampled material BRDF functions.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from raysect.core import AffineMatrix3D, Point3D, Vector3D
from raysect.optical import Ray, World
from raysect.optical.library.metal import RoughAluminium
from raysect.optical.material import UnitySurfaceEmitter
from raysect.primitive import Sphere
# Create scene graph
world = World()
ray = Ray(min_wavelength=499, max_wavelength=501, bins=1)
sphere = Sphere(100, parent=world, material=UnitySurfaceEmitter())
# Define Consts.
origin = Point3D(0, 0, 0)
material = RoughAluminium(0.25)
def calculate_brdf_surface(light_vector):
thetas = np.arange(0, 91, step=5)
phis = np.arange(0, 361, step=10)
num_thetas = len(thetas)
num_phis = len(phis)
thetas, phis = np.meshgrid(thetas, phis)
X = np.zeros((num_phis, num_thetas))
Y = np.zeros((num_phis, num_thetas))
Z = np.zeros((num_phis, num_thetas))
for i, j in np.ndindex(num_phis, num_thetas):
theta = np.deg2rad(thetas[i, j])
phi = np.deg2rad(phis[i, j])
outgoing = Vector3D(
np.cos(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)
)
# Calculate spectrum
spectrum = material.evaluate_shading(
world,
ray,
light_direction,
outgoing,
origin,
origin,
False,
AffineMatrix3D(),
AffineMatrix3D(),
None,
)
radius = spectrum.samples[0]
X[i, j] = radius * np.cos(phi) * np.sin(theta)
Y[i, j] = radius * np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta)
Z[i, j] = radius * np.cos(theta)
return X, Y, Z
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"}, layout="constrained")
for ax, light_angle in zip(axes.flatten(), [0, -10, -25, -45], strict=True):
light_position = Point3D(
np.sin(np.deg2rad(light_angle)), 0, np.cos(np.deg2rad(light_angle))
)
light_direction = origin.vector_to(light_position).normalise()
X, Y, Z = calculate_brdf_surface(light_direction)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap="viridis", edgecolor="none")
ax.set_xlim(-1, 1)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
ax.set_title(f"Light angle {light_angle} degrees")
plt.show()